Kubernetes is a container orchestration platform that provides the services and management features necessary to deploy, operate, and scale containers across a cluster or in a cloud computing environment. It has become a standard container orchestration method for organizations across a wide range of industries. This is especially true for organizations seeking to scale containerized applications.
It offers a flexible way to automate, deploy, and manage container workloads. Kubernetes storage is useful to storage administrators because it enables different forms of persistent, stateful data retention within Kubernetes cluster deployments, which are growing increasingly popular.
This article provides an overview of Kubernetes and persistent storage, how it works, and the benefits of using it.
What is Kubernetes?
To be clear, while Kubernetes storage is sometimes used in the cloud, it is a separate and distinct entity from cloud storage. Google created the Kubernetes platform in 2014 as an open-source effort to help manage the company’s container deployment. The platform moved to the Linux Foundation’s Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) in 2016 and is now a multi-stakeholder project supported by all major public cloud providers, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Oracle, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Kubernetes has become an important technology in recent years because of its portability. The same basic Kubernetes container that runs in one public cloud can be run in another with little or no change. The portability also enables multicloud deployments, where Kubernetes is used to orchestrate container deployments in more than one cloud platform.
Cloud native is another term often directly associated with Kubernetes, thanks in part to the fact Kubernetes is the foundational project of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation. In this case, cloud native refers to applications—storage or otherwise—built specifically for the cloud rather than being built for the data center and later ported to the cloud.
Application containers offer a way of packaging and delivering applications in a portable format. The most commonly used application container type with Kubernetes is a Docker container. With Kubernetes, multiple sets of containers can be deployed, scaled, and replicated for high availability and application stability.
Learn more: Kubernetes Review
Kubernetes Architecture: How Kubernetes Works
Kubernetes can be described as using a “master-worker” structure within a cluster of nodes. The master node acts as a control center, providing oversight of the cluster’s operation and overall state of the system. Operations include actions like scheduling, scaling, and generally orchestrating workloads across subordinate “worker” nodes that host the actual containers running applications. Master nodes typically communicate with worker nodes via API servers.
The Kubernetes architecture is designed with replication and availability as top priorities. There are several key elements included in any Kubernetes architecture:
- Kube Master: This is the primary control point for distributed orchestration across different nodes.
- Node: Nodes are the system resources that perform tasks as assigned by the Kube master.
- Pod: One or more containers can run inside a pod. Each pod gets its own IP address, network, and storage resources.
- Replication Controller/Replica Set: Ensures a specific number of pod replicas are running constantly.
- Services: Services include stable network endpoints for pod accessibility, which enable benefits like load balancing and service discovery.
- Deployments: Streamline the management and updating of applications with simple rollout, rollback, and scaling of replicas.
- ConfigMaps and Secrets: This function allows users to separate configuration data and sensitive information from the application code, enhancing security.
- Persistent Volumes: Allow users to store and access data past the lifecycle of individual pods.
- Ingress: Supports external access to services within clusters, serving as a gateway and enabling advanced routing and SSA termination.
Kubernetes allows developers to deploy and scale containers across a cluster or in a cloud computing environment.
How Persistent Kubernetes Storage Works
When Kubernetes was first developed, it was primarily used for stateless applications that did not have persistent storage requirements. Modern Kubernetes, however, is a different story and is fully capable of managing stateful applications and persistent storage.
There are several key concepts that are important to understand when it comes to Kubernetes storage. First, there is the container storage interface (CSI), which is the connection point for storage systems. Additionally, there are the storage enablement capabilities within pods, such as persistent storage objects, which can be used to request and connect to storage.
Container Storage Interface
The CSI is a relatively recent addition to Kubernetes, but it is one that greatly simplifies storage management and connectivity.
Prior to CSI, storage device drivers had to be directly integrated with the core Kubernetes code, which was a more time-consuming process for enabling new storage devices.The CSI provides an extensible plugin architecture that offers multiple benefits.
Key elements of the Container Storage Interface include the following:
- Extensible Plugin Framework: Storage drivers are plugins that are not hard-coded into Kubernetes.
- Updates: The CSI enables storage hardware and software vendors to more easily update drivers.
- Security: With CSI, there are improved security guarantees, due to a cleaner abstraction between Kubernetes and storage.
Kubernetes Persistent Storage Objects
While the CSI provides a way to connect storage devices to a Kubernetes cluster, support is still needed for Kubernetes applications to get access to storage. To that end, there are several key concepts for defining persistent storage objects:
- Pod: The pod can be used to mount a persistent storage volume into a container.
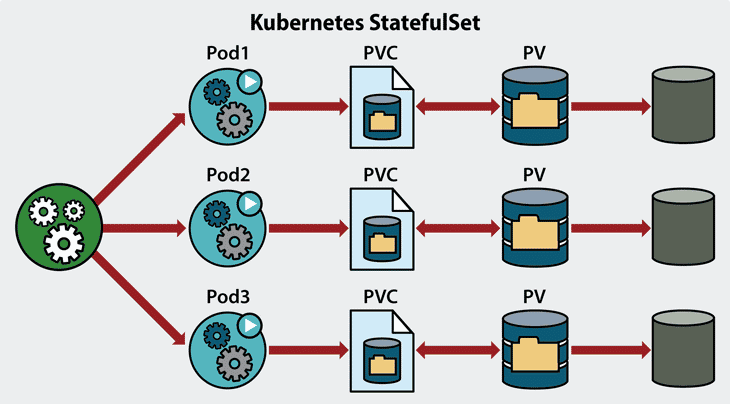
- PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC): When an application makes a request for storage, it is made as a PVC, which makes a storage volume usable in a pod. PVCs can be provisioned manually or dynamically via policy.
- PersistentVolume (PV): The PV is the administrative object for defining persistent storage in Kubernetes. PV provides a pointer to actual physical storage that is connected via the Container Storage Interface (CSI).
- StorageClass: The StorageClass object is a collection of PVs with the same characteristics, enabling an application to pull the right type of storage for a given deployment.
- StatefulSet: Since Kubernetes is built for resiliency, the StatefulSet object runs a configurable number of pod replicas, with each pod getting its own PVC from a PVC template. Each pod has a stable identity and can be scaled up or down.
The Benefits of Kubernetes
Kubernetes offers several key benefits to organizations seeking to upgrade their containerized application management process:
- Scalability: Because Kubernetes automates the scaling and distribution of workloads across clusters, applications can maintain high availability while meeting increased workload demands.
- Automation: The infrastructure and application configurations for Kubernetes are defined declaratively, as in specific instructions are used. This allows for simple replication, versioning, and automation.
- Efficiency: Kubernetes can introduce increased resource efficiency by optimizing resource allocation, reducing costs, and maximizing performance.
- Container Portability: By effectively ignoring underlying application infrastructures, Kubernetes applications can run across different environments, which is an especially valuable benefit for organizations using hybrid network setups that include on-prem data centers and cloud resources.
- Self-Healing: When Kubernetes discovers a failing container, it can automatically restart or even replace it, adding resiliency and fault tolerance.
- Community Support: As an open-source resource, Kubernetes benefits from constantly evolving community input, new plugins, and the latest tools and best practices.
Bottom Line: Kubernetes and Persistent Storage
Kubernetes is a rapidly developing technology that has been embraced by cloud vendors and enterprises alike to enable a more agile and scalable form of application delivery. With a properly implemented Kubernetes storage configuration, databases and application data can be created and accessed by many applications, enabling greater speed and efficiency.
Read next: Top 8 Kubernetes Alternatives