Learn about the benefits and drawbacks of using NVMe over Fibre Channel. Explore how this technology can improve your storage performance.


NVMe over FC is a technology specification that uses nonvolatile memory express (NVMe) commands to transfer information and data over a high-speed Fibre Channel (FC) connection, accelerating data transfer speeds for storage area networks (SANs) or cloud-based storage. By enabling the NVMe protocol to be used over FC and Ethernet connections, it allows faster connectivity between storage devices and servers. This article explores how the technology works and details its uses and benefits.
Historically, SANs used three protocols to transfer data: internet small computer systems interface (iSCSI), serial attached SCSI (SAS), and Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP). But the shortcomings of these protocols became apparent when they proved unable to support the full potential of high speed solid state storage.
The solution was NVMe, a new storage access and transport protocol specifically designed for solid state drives (SSDs), all-flash storage arrays, and other solid-state storage technologies. Here’s an overview of the individual and combined technologies:
NVMe-over Fibre Channel (NVMe-FC, or NVMe over FC) uses NVMe-based message commands to transfer data and status information between a host computer and the target storage system. These commands are transmitted by being encapsulated within a Fibre Channel frame and routed to Fibre Channel switches.
When a host computer initiates an action to a target storage system via a server, the FC switch detects a Start-of-Frame (SOF) delimiter and creates an interaction between initiator and target on the Fiber Channel network. FC frames are lossless—no frames are dropped or lost in transit between the initiator and the target.
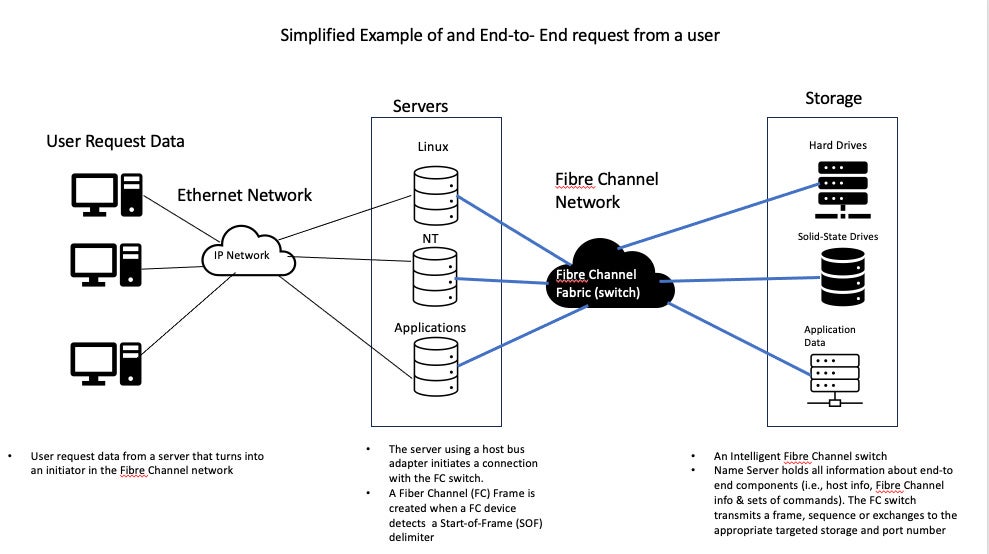
NVMe-FC is reliable and efficient for supporting enterprise data centers hosting critical applications. It reduces latency, improves performance, provides better input/output processing, and handles demanding workloads very efficiently.
When used in high speed environments like data centers, NVMe-FC can make it possible to process big data, analytics, deep learning, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) efficiently and predictably, making it the top choice for businesses executing business intelligence operations.
NVMe over FC is known for its high reliability and performance, making it an ideal option for any enterprise running round-the-clock mission-critical applications. For example:
NVMe over FC is a highly scalable solution for enterprise organizations using solid-state storage technologies. It improves the performance of traditional protocols and exceeds that of non-FC networks—SCSI protocol performance and latency over a NVMe-FC network is better than a SCSI protocol executed on an FC ecosystem.
Overall, NVMe-FC offers the following benefits:
Because NVMe-FC provides overall performance improvements while still using traditional protocols, it allows an organization to migrate to the NVMe-based network without the urgency of replacing its current infrastructure.
Fibre Channel networks are dedicated ecosystems, and as such, they’re far more expensive than an Ethernet network. They also require skilled personnel to maintain them due to the specialized equipment involved.
NVMe-FC also does not support multipath, a performance-enhancement technique that uses more than one physical path between a CPU and storage devices for redundancy, dynamic load balancing and reconfiguration, and automatic path management. This can be overcome by employing other network options to ensure the reliability of the NVMe-FC ecosystem remains—for example, redundant physical and logical paths to prevent single points of failure.
Any organization involved in real-time analytics or data processing, online transaction processing, online analytical processing, or hosting mission-critical applications can gain a competitive edge using an NVMe-FC network. NVMe-FC can be used in any industry—including healthcare, retail, finance, and airlines—for a wide range of applications from minimizing financial losses to saving lives. By providing faster speeds, reduced latency, and better reliability, it maximizes the efficiency of storage area networks and facilitates high-speed data processing.
Read Types of Enterprise Data Storage to learn more about the technologies businesses use to store the vast amounts of data on which they rely.


Don Hall is a contributing writer to Enterprise Storage Forum, where he covers data storage technology, storage hardware and software, and data networking. He worked for more than two decades as an IT Supervisor for the federal government and as IT Operations Supervisor for an IT Military Command managing programmers, cybersecurity staff, and infrastructure and networking personnel. Previously he worked as an application programmer. Don earned a B.S. in Business Information Systems from San Diego State University and has certificates in Technical Communication and web development with an emphasis in Java/Open Source. He has also had an active CompTIA Security + (ce) since 2011, and a Network +(ce) since 2015.

Enterprise Storage Forum offers practical information on data storage and protection from several different perspectives: hardware, software, on-premises services and cloud services. It also includes storage security and deep looks into various storage technologies, including object storage and modern parallel file systems. ESF is an ideal website for enterprise storage admins, CTOs and storage architects to reference in order to stay informed about the latest products, services and trends in the storage industry.
Property of TechnologyAdvice. © 2026 TechnologyAdvice. All Rights Reserved
Advertiser Disclosure: Some of the products that appear on this site are from companies from which TechnologyAdvice receives compensation. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site including, for example, the order in which they appear. TechnologyAdvice does not include all companies or all types of products available in the marketplace.